All The Vegetables That Start With U
Important Note: When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Content, pricing, offers and availability are subject to change at any time - more info.
Among the essential parts of our meals are vegetables. Vegetables provide many nutrients that our body needs to function well and prevent us from suffering from certain illnesses. The letter U is rarely used in English dictionary, and therefore all the vegetables that start with the letter U are just but a handful of vegetables. The list of vegetables that start with the letter U will help you quickly navigate unfamiliar and familiar vegetables and boost your knowledge of vegetables worldwide. You will need a list of vegetables that start with the letter U so that you can know the origin of the vegetables, where they are commonly grown, how they taste, their scent, how to prepare them, and where you can purchase them in America, their nutritional value, and even the potential health benefits you will gain from eating the vegetable. The list of vegetables starting with the letter U contains ube, Umatilla russet potato, Udupi Mattu Gulla eggplant, urad bean, Ukrainian heart tomato, ulluco, ulster emblem potato, and upland cress. Here is a detailed and well-described list of all the vegetables that start with the letter U:
- Ube
- Udupi Mattu Gulla Eggplant
- Ulluco
- Ulster Emblem Potato
- Umatilla Russet Potato
- Upland Cress
- Urad Bean
- Umibudo
- The Final Letter
Ube
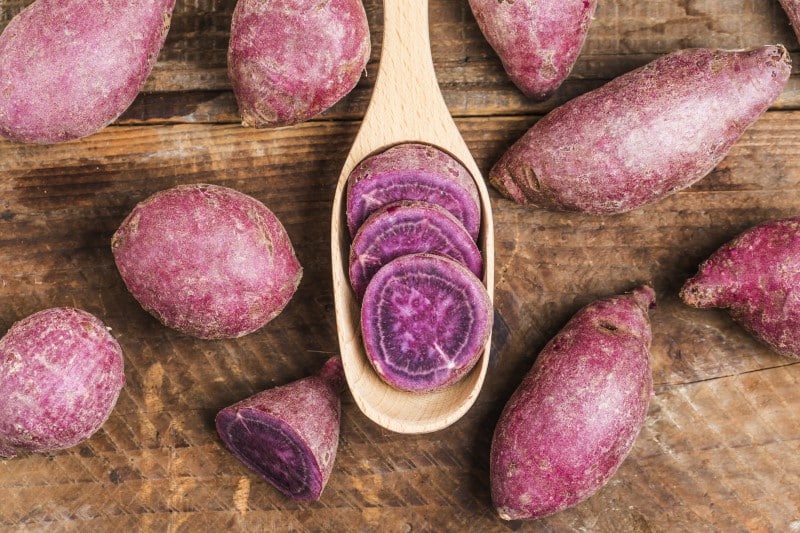

The scientific name of ube is Dioscorea alata. The ube vegetable is also known as purple yam, water yam, violet yam, and ube halaya. Ube is a variety of tuber popular for its color, which is deep purple. The deep purple color of the ube’s skin and flesh gives the vegetable a stunning appearance. It is, however, sometimes white. The purple yam looks very similar to a sweet potato. Ube has a cylindrical shape, with the flesh having a watery texture. The root vegetable slightly resembles sweet potatoes and taro. The deep purple in ube indicates that it contains high levels of anthocyanins. The tuberous vegetable is highly appreciated fir its distinctive hue. Ube originated from the Philippines but has currently grown popular in America. In the Philippines, it grows in areas such as the central Visayas, northern Luzon, Northern Mindanao, Southern Tagalog, and Bicol. The used plant is a perennial plant that climbs. You can only get ube in particular seasons, and they are usually in short supply. This makes it have high demand and be a bit pricey compared to other root vegetables.
You can use ube as an ingredient to make desserts such as muffins, cheesecakes, and ice cream. The sweet flavor of ube makes it a perfect choice for making desserts. The vegetable originated from the Philippines but has spread widely to be an international sensation. The unique colored root vegetable has a sweet and starchy flavor. It is a rich source of nutrients like fats, sodium, protein, calcium, iron, vitamin C, and A.
When it comes to flavor, ube is not as sweet as the regular sweet potatoes. It also does not gain a soft and moist texture when cooked. The taste of ube is mellow, nutty, and almost like that of vanilla. Some people dispute the vanilla taste and claim ube’s taste is closer to that of a coconut.
It is not as easy to get ube in America, unlike the sweet potatoes. It might take you a good amount of time searching for ube to get it at a grocery store. You will most likely get its products rather than a whole tube if you get it. The products of ube include ube extract, ube powder, and frozen ube. Ube is an excellent choice for people with sweet tooth. To prepare ube, you can bake it, mash it, steam it, boil it, or even roast it.
Consuming use has health benefits for its users, such as performing anti-oxidative properties, hypo-glycemic properties, and anti-microbial activities. The anti-microbial activities are supported by the content of resistant start in ube and help deal with constipation. To find ube in the United States is not easy. You can purchase them at local grocery stores for Asians and farmer’s markets.
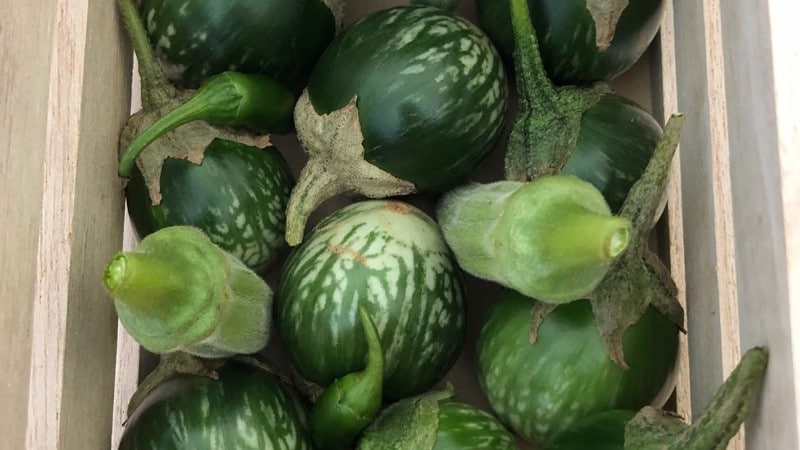
Udupi Mattu Gulla Eggplant
The scientific name of Udupi Mattu Gulla eggplant is solanum melongina var esculenta needs. The vegetable originated from India in a village called mattu and has been used for uncountable years. It is a type of eggplant and heirloom vegetable. The vegetable is also called Gulla and Udupi brinjal. It is commonly used in south Indian dishes. The vegetable is large and with a round shape. The skin of Udupi mattu Gulla eggplant is thin and with light green stripes. The vegetable has a few seeds and a good quantity of pulp.
Udupi mattu Gulla eggplant has some thorns on its stalk that differentiates it from other varieties of Gulla. The Udupi mattu Gulla eggplant has a thick skin that dissolves when you cook it. This vegetable is exclusively grown in villages in the Udupi district. It has taken the effort to retain the vegetable’s authenticity. The distinctive taste and flavor have made it a favorite ingredient when making Udupi cuisines such as curry. Udupi mattu Gulla eggplant is a rich source of iron. It has a thick pulp, very few seeds, and a thin skin.
Ulluco
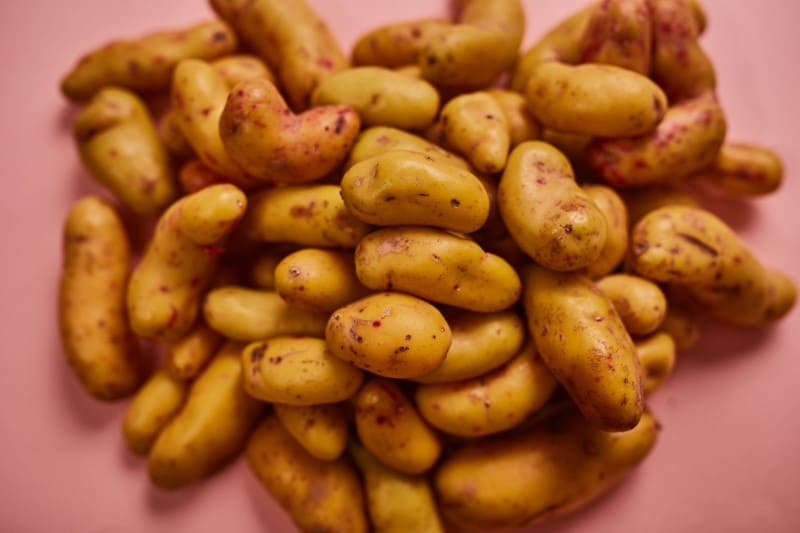

The scientific name of ulluco is Ullucus tuberosus. Ulluco is a flowering plant that belongs to the Basellaceae family and the Ullucus genus. It is a popular vegetable in a few South American countries. The parts of ulluco that are eaten are the tubers and sometimes the leaf. Ulluco tastes like spinach. The flavor of ulluco is sweet and unique.
Ulluco is cultivated to serve as both a root and leafy vegetable. Although, it is mainly grown and consumed as a root vegetable. You can consume its tubers, leaves, and stems. The vegetable originated from the central Andes of Bolivia and Peru and has existed for over 4000 years. It is widely grown for commercial purposes in South America’s Andean region. The vegetable is also known as ulluku, papa Lisa, ulluma, ruba, chungua, and olluco.
Ulluco is a rich source of calcium, carotene, and protein. The starchy tubers have smooth skin, and their shape can either be elongated or spherical. Its size is the same as that of a regular potato, but it can grow to a length of up to 15 centimeters. It looks like a small potato but more elongated, round, and colorful. Ulluco has waxy and brightly colored skin with various colors such as purple, pink, orange, reddish, and yellow. Eating ulluco will add up your body with nutrients such as vitamin C, carbohydrates, and protein.
To enjoy the tasty flavor of ulluco, you can use it as an ingredient to make stews, soups, and salads. It is not recommended for baking and frying when cooking ulluco because it has high water contents. Ulluco is usually cut into small strips to increase its shelf life. Even after cooking ulluco, it will still have its crisp, almost crunchy texture. The vegetable is rarely consumed raw and is usually cooked first. Ulluco is not susceptible to pest and disease problems.
Ulster Emblem Potato
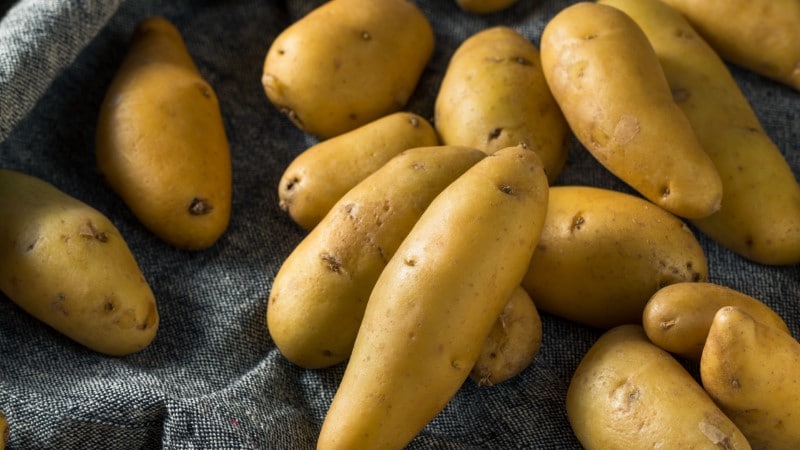

The scientific name of the Ulster emblem potato is Solanum tuberosum. It belongs to the Solanum genus family. Ulster emblem potato is also known as fingerling potato and creamer potato. This variety of potatoes originated in Ireland around 1966. Its skin is pale-colored. It also has a pleasant flavor. Ulster emblem potato’s shape is long and oval compared to common potatoes. The skin and flesh are white with a semi-waxy texture. It produces flowers that have a pink and violet color. Ulster emblem potato has a good and reasonable flavor. The flavor that the ulster emblem potato offers is not too strong. Ulster emblem potato stands out as a plant that produces a high yield and has a long shelf life. To preserve the tubers fresh, keep them in a cool and dry place.
Intake of ulster emblem potato can help health benefits such as performing anti-oxidant activities and improving digestion in the body. However, you should be keen not to overconsume as it increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Umatilla Russet Potato
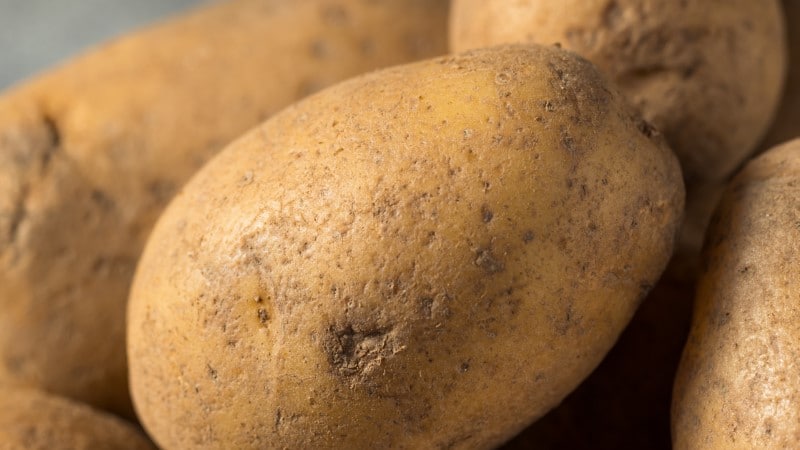

The scientific name of the Umatilla russet potato is Solanum tuberosum L. cv. Umatilla Russet. The vegetable belongs to the Solanum genus. This variety of potato was given its name after the Umatilla tribe by the Oregon State. Umatilla Russet potato is native to the United States. It was released jointly in 1998 by Idaho, Washington, the USDA, and Oregon. The vegetable got its name after a native American tribe.
You can use the Umatilla russet potato to make French fries. French fries made from Umatilla russet potato have a superior taste, flavor, and color. The tuber vegetable has a phenomenal flavor that you will enjoy and a creamy texture. The tuber’s skin has a tan color and looks like a russet. It is long and tends to have tapered apical ends. The leaves of a Umatilla russet potato are dark green, and its flesh is a bit creamy. Flowers produced by the Umatilla russet potato, usually about seven per plant, are light purple with a central cone colored yellow to orange.
The vegetable is less susceptible to many pests and diseases. Umatilla Russet potato is very easy to grow and is reliable. The quality of this vegetable can resist diseases, making it easy for farmers to grow and cultivate it. Growing and cultivating Umatilla russet potato is just like regular potatoes. When comparing Umatilla russet potato to the regular potatoes, they are smaller. They also take longer to grow and mature, unlike the regular tuber potatoes.
Storing Umatilla russet potatoes will take a long time to start rotting, but they can have bruises or black spots on the potato skin.
Upland Cress
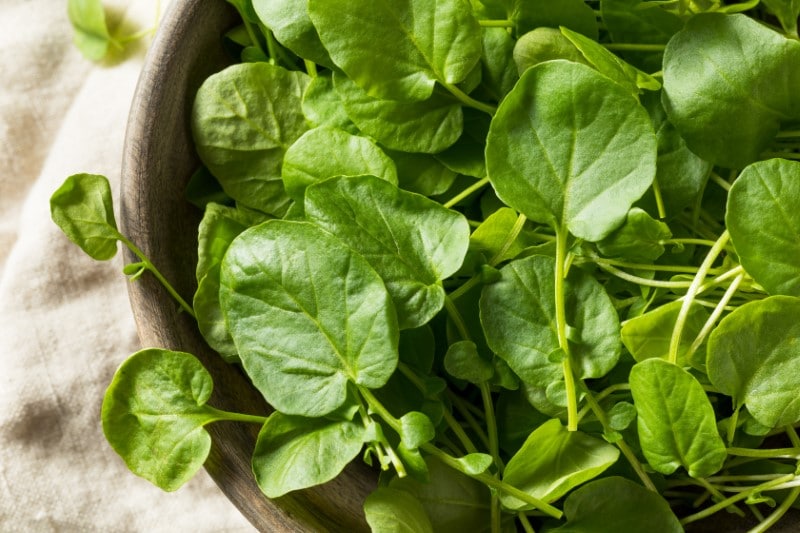

The scientific name of the upland cress is Barbarea verna. It is a leafy vegetable that has been grown in England for several hundreds of years. Upland cress does not need a lot of water. It is also known as land cress, cassabully, Belle isle cress, early yellow rocket, American cress, black wood cress, bank cress, creasy salad, and dryland cress. Upland cress belongs to the Cruciferae family and the Barbarea genus. The vegetable originated from western Asia and southern Europe. It has been grown in Europe as a vegetable since the 17th century.
The appearance and taste of upland cress are similar to that of watercress, but they are different vegetables. It has tiny leaves that are close to being square-shaped. Even its flavor and nutrient density are similar to watercress. The difference between upland cress and watercress is that upland cress has more tender stems and thinner leaves than watercress. The plant that produces upland cress has leaf stems about eight inches long. You can use upland cress as an ingredient to make soups, sandwiches, and salads while raw. The upland cress is prepared like regular vegetables such as kales.
Growing and cultivating upland cress is mostly done during the cooler months of the year. It can be grown in almost all garden soils. The vegetable is sold with its roots still attached to it. The roots help with the vegetable’s shelf life, and therefore you should not cut them until you are ready to use them. Also, splash the roots with water regularly to avoid them from drying out. The vegetables can have a longer shelf life if you put them in a fridge.
The majority of the time, the upland cress grows like a weed. Although grown and cultivated has similar growing habits to watercress, it is way easier to grow. It nourishes in a cool environment, a place with partial shade and moist soil. You should sow it regularly to have an unlimited and continuous supply of upland cress. You can easily grow upland cress in your home garden and start harvesting when it is about four inches high. To harvest, you pick the upland cress leaves from the plant and leave the roots and stem intact to allow it to form more leaves.
Upland cress has edible leaves with a sharp taste. The leaves have a small serration on their leaf margins. It has a stronger peppery flavor than watercress. The best part about the upland cress is that all its parts are edible. Due to its close similarities to watercress, when you need to purchase upland cress, you should refer to it by its botanical name, Barbarea verna.
The biennial herb, just like watercress, loves water. However, the upland cress will not yield well if it is partially submerged in water for a long period. Otherwise, the vegetable needs frequent watering and full sun.
Urad Bean
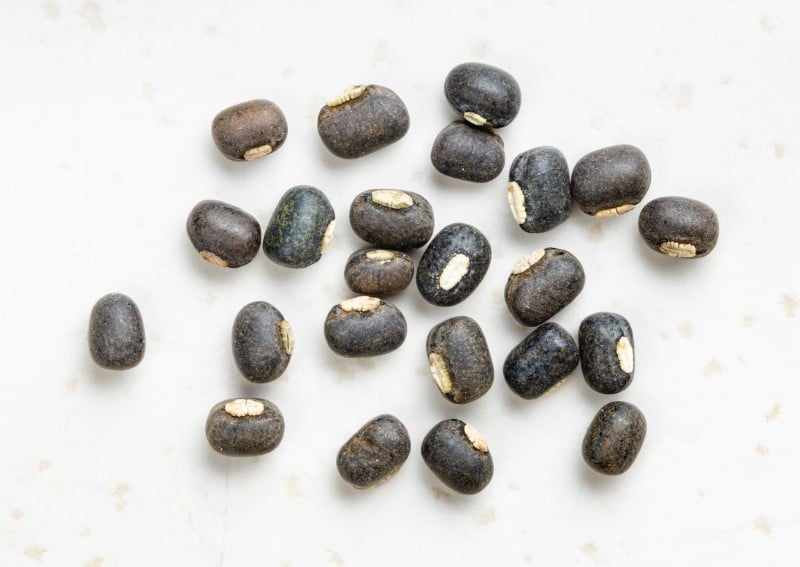

The scientific name of urad bean is vigna mungo. Urad bean belongs to the Fabaceae family and the genus of vigna. Urad bean is a type of lentil. This bean is common in south Asian parts, especially in India. It is native to South Asia. It can also be enjoyed whole.
Urad bean is also known as mash Kalai, uzhunnu parippu, black gram, ulundu paruppu, uddu, black matte, udad dal, minumulu, and minapa Pappu. The urad bean usually has black skin, and on the inside, when split, is white. The inside can sometimes be pale yellow. It contains a little bit of a glutinous texture. It is used as an ingredient to prepare Indian cuisines such as curry, dosai, and idlee. Dosai are pancakes made in India, while idlee are dumplings made in India using fermented urad beans.
Urad beans do not have a strong smell when raw or cooked. However, if you soak urad beans in water for some time, they ferment because of the build of bacteria. This will not make the beans unhealthy to consume, but they will emit an unpleasant smell. The taste of urad beans is highly dependent on whether it has skin or it is skinless. Those that have been removed from their skin have a bland taste, whereas the urad beans with their skin on when cooked contain a strong flavor.
If you do not have urad beans, mung beans, azuki beans, and pigeon beans can work well as a substitute. The plant that produces the urad bean is a densely-haired bush, erect, and grows yearly. Urad bean pods are cylindrical, narrow, and reach about six centimeters long. It is highly valued because it is dense in terms of nutrition. It is a rich source of carbohydrates, calcium, iron, calcium, protein, vitamin A, vitamin C, dietary fiber, zinc, and potassium.
To buy urad beans in the United States is not as easy as the regular vegetables. You can purchase them at Indian markets in America. The urad beans are available in many forms, whole beans with their skins on, whole but skinless, split beans with their skin, and split beans without their skin. Urad flour made from urad beans is also common.
People use urad beans for beauty care, where it is used to nourish the skin and give it rejuvenating properties. It is said that it helps keep the skin soft, moisturized, and glowing. It also works well as a body scrub where you can use it for skin exfoliation and removal of dead skin cells and dry skin. Urad beans can also help remove extra oil in your skin and reduce pimples and acne. Apart from the many ways urad beans can improve your skin, consuming them has potential benefits. It can perform anti-inflammatory activities, maintain the heart’s health, and improve the immune system.
Umibudo
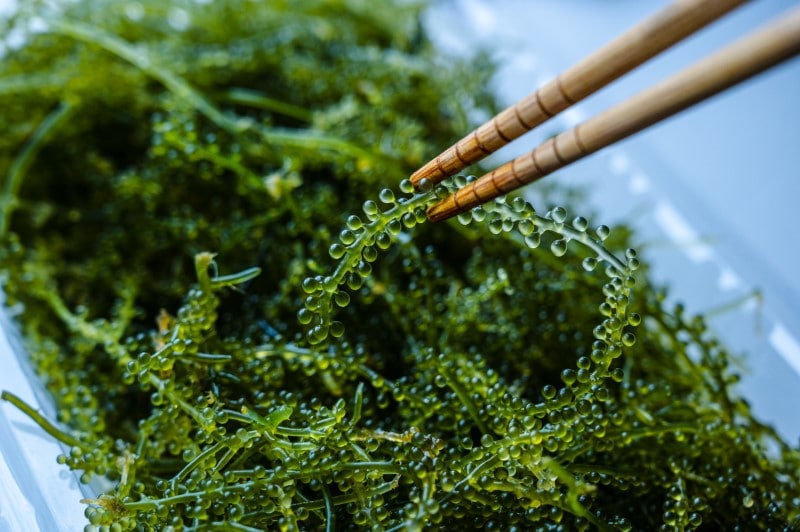

The scientific anme of umibudo is Caulerpa Lentillifera. It is also known as grape seaweed, lato, longevity seaweed, arose, and latok. This variety of vegetables contains high nutritional levels.
Umibudo can be enjoyed raw or cooked. To enjoy the full capacity of the nutrients in the grape seaweed, you should eat it raw instead of cooking it. Cooking will tone down the vegetable’s crispiness and flavor. You can eat Umi budo as an ingredient in recipes such as salads and sauce. Umibudo can offer a great option for a snack by soaking the vegetable in water to desalinate and then eating it.
The Final Letter
This list will help you play a guessing game of the vegetables that start with the letter U. Enjoy this extensive list as you prepare some tasty and international meals. When you finish reading this article, you will be able to identify vegetables simply by their appearance, taste, or smell. This glossary will make you look vegetable smart and help you diversify your daily diet. This post will push you to try out new interesting recipes.