All The Vegetables That Start With V
Important Note: When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Content, pricing, offers and availability are subject to change at any time - more info.
Vegetables are a must-have in your diet, but there are so many types of vegetables available that you can’t keep track of all of them. So, to help you keep track of the vegetables you eat, you can create a list of all vegetables; this will help you make an informed choice about all your meals and promote healthy living. To help you with your list, here is a list of all the vegetables that start with V.
- Variegated Screw Pine
- Vegetable Mustard
- Vainita
- Vegetable Hummingbird
- Vegetable Marrow
- Velvet Bean
- Velvetleaf
- Verdolaga
- The Final Letter
Variegated Screw Pine

Variegated screw pine is a perennial plant belonging to the Pandanaceae family. The scientific name of the variegated screw pine is Pandanus tectorius. In some regions of the world where variegated screw pine is cultivated, it is known by different names such as pandan, screw palm, or screw pine. Variegated screw pine is native to the tropic and subtropic regions of the world, but it is mainly found in Malaysia and Madagascar. Though the variegated screw pine is mainly referred to as pandanus palm, it has no relation whatsoever to palm trees.
There are a variety of species of the variegated screw pine, and they happen to differ in size from the small shrubs that grow to a height of less than a meter to the medium-sized trees standing at the height of about 20 meters with a moderate growth rate and a broad canopy. The tree trunks of the variegated screw pine happen to be stout and covered with plenty of leaf scars. The top of the tree is made up of one or more strap crown-shaped leaves that are spiny.
Variegated screw pine is mainly cultivated for its unique scent and taste. The edible part of the variegated screw pine is the leaves which are mostly consumed as either powder or paste, and sometimes the leaves are mixed with a water extract and turned into essential oils. In some regions, the leaves are also consumed as a vegetable or used as an ingredient in preparing some dishes, especially in South and Southeast Asian cuisines. In Sri Lanka, the leaves are a staple vegetable and are also used in the preparation of most meat dishes. In Malaysia and Indonesia, the variegated screw pine leaves are added to curry and rice dishes such as nasi lemak, while in the Philippines, the leaves are paired with coconut meat to make desserts and beverages like gulaman and Maja Blanca. In Indian cuisines, kewra, an extract distilled from the flowers of the variegated screw pine, is used to flavor various drinks and desserts.
Variegated screw pine is a rich source of vitamin A which is essential for your eye health and contains properties that help prevent certain types of cancer. Other health benefits of variegated screw pine include acting as a joint and arthritis pain reliver due to the presence of some phytochemicals that are renowned pain relivers. Variegated screw spine contains carotenoids class of antioxidants that help reduce the risks of developing atherosclerosis. When crushed, the leaves of variegated screw spine are known to treat skin problems, minor burns, and sunburns. Also, variegated screw pine is known for its blood sugar control properties.
Vegetable Mustard

Vegetable mustard is known by various names in different regions worldwide; these include Chinese mustard, Indian mustard, brown mustard, leaf mustard and oriental mustard. Scientifically vegetable mustard is referred to as Brassica juncea. Vegetable mustard is a member of the cruciferous vegetable family. Vegetable mustard is divided into four subgroups: juncea, tsatsai, napiformis and integrifolia.
The edible parts of the mustard vegetable plant are the leaves, stems and seeds. Vegetable mustard is very popular in African, Italian, Chinese, Bangladeshi, Korean, Nepali, South and North American cuisines, whether through the oils, leaves or stems. Vegetable mustard can be eaten raw or cooked, but its flavor will mainly depend on how it is prepared and what is used to accompany the meal. In Nepal, the tsatsai variety is used to make a Nepali pickle known as achar, and in Chinese cuisine, the pickle is known as zha cai. In India, the whole plant is used to make a dish known as Sarson da saag. In Japanese cuisine, vegetable mustard is known as Akana and is pickled for use as a condiment or a filling in onigiri. In Southeast Asia, a dish known as kiam chai boey is made by stewing vegetable mustard with meat on the bone, tamarind and dried chili.
Just like other green and leafy vegetables, vegetable mustard is a rich source of health-boosting nutrients such as vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, C, K and A, and minerals like calcium and potassium. These nutrients help the body by boosting the immune system, lowering the risks of chronic diseases, protecting the body cell from damage caused by free radicals, improving the body functions, maintaining and promoting healthy bones, and improving the brain function. Vegetable mustard can be found in almost all grocery stores across the United States. Also, sometimes farmers tend to grow vegetable mustard as green manure. Due to the high tolerance of vegetable mustard towards heavy metals, it’s sometimes used to extract the heavy metals from the soil in hazardous waste sites.
Vainita
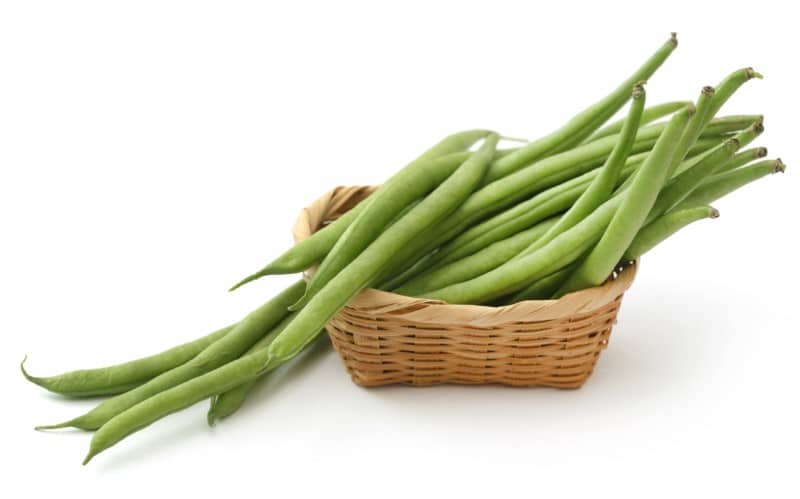

Vainita is popularly known as green beans, which are young unripe fruits of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) that are mainly harvested to be consumed as a vegetable. Vainita is referred to by different names depending on the region they are cultivated. These names include French beans, green beans, snap beans, and snaps or string beans. In the Philippines, vainita are referred to as habichuelas or Baguio beans. Vainita is native to America. However, they grow worldwide all year-round, meaning you’ll find them in grocery stores no matter what season it is. The high season for vainita harvesting is usually between May and October. The difference between vainita and other beans is that vainita is harvested and primarily consumed while still green and in their pods.
Vainita is a versatile vegetable and can be prepared differently depending on the region. Vainita can be prepared by either steaming, baking, boiling or stir-fried. However, Vainita is mainly cooked in dishes like stew, soups and casseroles. In the United States, vainita is a popular dish during Thanksgiving as green bean casserole, while some restaurants serve vainita fried and battered as green bean tempura. In most countries, Vainita is sold canned, frozen or fresh. In some regions, vainita is dried or fried with vegetables such as corn, carrots and peas and sold as vegetable chips.
Vainita is a rich source of proteins, folate, magnesium, vitamin B, potassium, iron, fiber, and antioxidants, including vitamin C, quercetin, kaempferol, and flavonols. These nutrition contents of the green bean have various health benefits, such as lowering the risk of cancer and lowering cholesterol levels. Due to its low glycemic index, vainita is regarded as diabetes-friendly. Folate is essential to expecting women since it aids in the development and growth of the unborn baby. The vitamin B in vainita also helps reduce the signs and symptoms of depression. The antioxidants present in vainita help the body fight free radicals, which helps to lower your risk of some health problems and reduce cell damage. Also, vainita is rich in iron, thus helping in preventing anemia.
As much as vainita is beneficial to your health, it is vital that you also know some of the risks associated with them. For example, if you are taking blood thinners, you are advised to watch your vainita intake since the vitamin K may interfere with the medication, thus altering how your blood clots. Also, vainita contains phytic acid, which can bind with some minerals, thus preventing their absorption into the body.
Vegetable Hummingbird
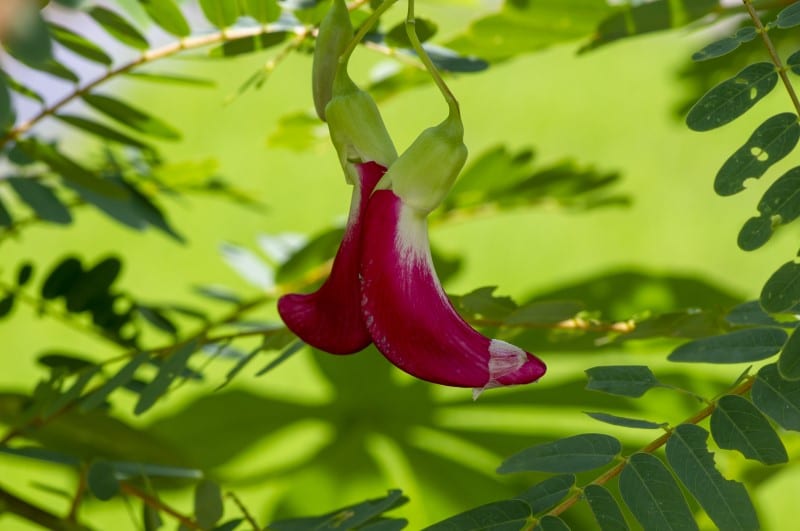

Vegetable hummingbird is a small leguminous plant native to Northern Australia and Southeast Asia, especially in the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia and Brunei. The scientific name of vegetable hummingbird is Sesbania grandiflora. Vegetable hummingbird is also known as agati, West Indian pea and katurai. Vegetable hummingbird is heavily cultivated in most parts of Sri Lanka and South India. Vegetable hummingbird is cultivated primarily for its edible flowers and leaves. The taste of vegetable hummingbird is usually astringent and bitter. Vegetable hummingbird mainly grows in regions experiencing a hot, humid climate and have good loamy soils.
The flowers of the vegetable hummingbird are a staple vegetable in the Southeast Asia region of Vietnam, Laos, Thailand and the Philippines. In Cambodia, the flowers of the vegetable hummingbird are known as angkea dei; when mixed with the leaves, they are used to make curries such as Samlor mchou angkea dei and salad sauces like toek kroeung and bok amproek. In Thailand, the flowers are eaten either blanched with a spicy chili sauce known as nam phrik or raw. Also, in Thai cuisine, the flowers are used to prepare curries like Kang som. The flowers are a popular delicacy in India and Bangladesh, especially after being fried with gram paste. The young pods of the vegetable hummingbird are also edible.
Vegetable hummingbird is full of nutritional content such as vitamin C, B2, B1 and B9, iron and selenium. These nutritional contents enable the body to maintain blood pressure at the required levels while keeping the arteries flexible. Vegetable hummingbird also promotes normal fetal growth in pregnant women. Other health benefits include clear skin, boosting the body’s immune system, reducing the risks of Alzheimer’s, treating diabetes and preventing regular migraine attacks.
The barks and roots of the vegetable hummingbird plant are renowned for their medicinal properties. Vegetable hummingbird is also used to treat certain smoke-related complications. Also, the extract obtained from the leaves of vegetable hummingbird contains aspartic acid and linolenic acid. These acids are the primary compounds responsible for the anti-glycation properties of the vegetable hummingbird leaves, making the leaves an ingredient in manufacturing high-end glycation end-products.
Vegetable Marrow
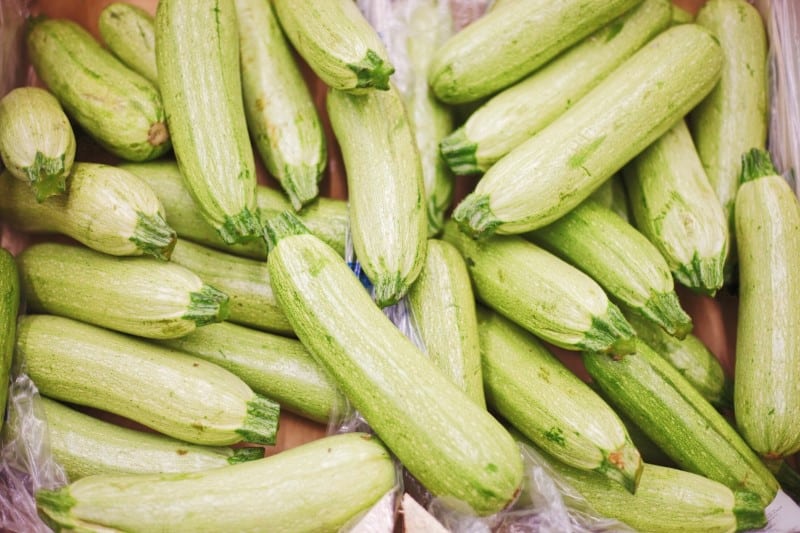

Vegetable marrow is scientifically known as Cucurbita pepo. Vegetable marrow is an annual herbaceous plant belonging to the Cucurbitaceae family. Vegetable marrow is very popular in European countries like Britain, Ireland, the Netherlands and France. Vegetable marrow is regarded as an immature, edible fruit of the Lagenaria, an African cucurbit gourd. Vegetable marrow is believed to have originated from Mexico and Central America. Vegetable marrow is mainly cultivated in the Americas, Britain and some parts of Europe, where it is popular. For quality yields of vegetable marrow, they require to be grown in areas experiencing warm climates and with rich, well-drained soils.
Vegetable marrow can grow to about 9 to 18 inches. Just like its relative vegetables, marrow is usually oblong, green with a neutral flavor and a firm rind. The inner flesh of a vegetable marrow is typically white or creamy. It is vital that the vegetable marrow is harvested before they over-ripen since if they are left to overripe and grow too long, they eventually become bitter. Vegetable marrow can be eaten either raw as salad or cooked. There are various ways of cooking a vegetable marrow. You can cook it by either frying, grilling, sautéing, baking, pickling or using it as stuffing. Flowers and seeds of the vegetable marrow plant are also edible. The seed can be dried and then ground into flour which may be used in baking, or they can be eaten directly or ground into a paste. However, for the seeds to be eaten directly, they have to be from a young vegetable marrow since the mature seeds are usually very hard.
Vegetable marrow provides a host of nutrients that are essential to the body, such as vitamin C, K, B6 and A and minerals like potassium, manganese, phosphorus, calcium, iron and copper. Vegetable marrow is also a rich source of beta-carotene, which is a very potent antioxidant. The health benefits of these vitamins, minerals and antioxidants include assisting in digestion, helping to prevent certain types of cancer, inflammation and anemia, boosting the body’s immunity and treating diabetes. Vegetable marrow is a popular vegetable in the Americas and can be found in almost all grocery stores in the United States.
Velvet Bean
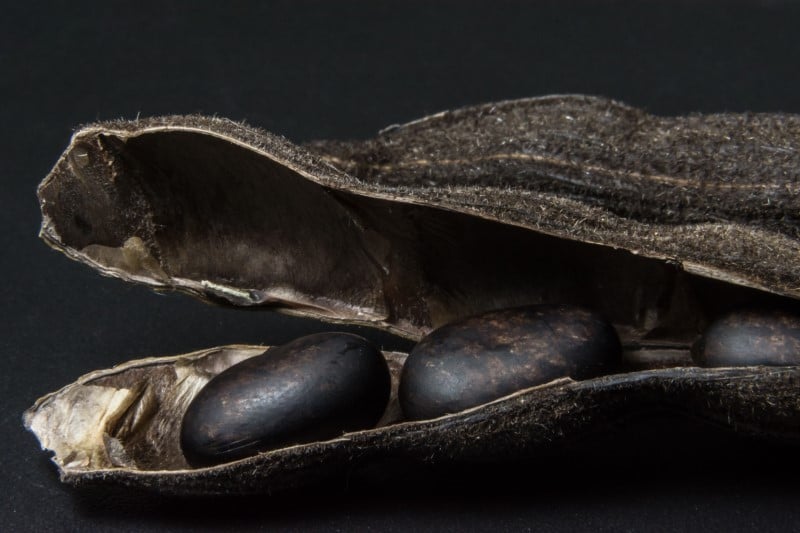

The velvet bean is an annual tropical legume that is referred to as Mucuna pruriens in the scientific community. Other popular names for the velvet bean are monkey tamarind, Yokohama velvet bean, Mauritius velvet bean, Bengal velvet bean, cowitch, lacuna bean, cowage and Lyon bean. Velvet bean is widely known for the itching sensation that occurs when contact with the plant is made. The velvet bean is native to Africa and Asia though it is heavily cultivated in various regions of the world.
The flowers of the velvet bean plant are usually lavender, purple or white. The seed pods can grow to about 10 centimeters long and are covered in loose orange hairs. The hairs contain a protein known as mucunain that is responsible for the itching sensation caused by the plant. The velvet bean seeds are usually brown and drifty or black and shiny.
The beans of the velvet bean plant are edible, but they have to be cooked first. The beans have to be soaked before boiling or cooking them since they contain toxins harmful to humans. The soaking of the beans should last for about 30 minutes to 48 hours, and the water should be changed at intervals of about three hours. Once dried, the velvet beans can be ground into flour which can be used in baking or cooking. An example of a dish prepared with velvet bean flour is velvet bean tortillas.
The health benefits of velvet bean include treating diabetes and improving the sperm count in males. The serotonin content in velvet bean is helpful to individuals undergoing Parkinson’s disease treatment. Velvet beans help increase potency through stacking and relieving stress. Velvet beans also possess various sexual benefits like boosting libido in both males and females, and it also acts as an aphrodisiac.
Velvetleaf
Velvetleaf is an annual plant belonging to the Malvaceae family and is scientifically known as Abutilon theophrasti. The velvetleaf is also known by other names such as Chinese jute, crown weed, buttonweed, China jute, lantern mallow, pie-maker, butterprint or velvet plant. The velvetleaf is native to the southern regions of Asia.
The velvetleaf plant can grow to a height of about 8 feet. The stems of the velvetleaf are mostly covered by downy hairs. Velvetleaf produces flowers that are predominantly yellow and contain up to five petals. The flowers usually grow on a stalk and mostly grow in a cluster. The plant also produces seeds that are encased in a pod. When the seeds reach the maturation stage, the pods burst open, thus releasing the seeds.
The leaves and seeds of the velvetleaf are edible, and they possess a somewhat minty flavor. The leaves can be prepared by stir-frying or in an omelet to improve the taste and aroma. In the Maldives, velvetleaf leaves are used in traditional Maldivian cuisines. An example is in the preparation of mas huni, a Maldivian dish made up of fish mixed with grated coconut and chopped velvetleaf. In China and the Kashmir region of India, the seeds are consumed raw only when they are still young. When mature, the seeds are dried and then ground to be used in preparing various kinds of soup and baking bread.
The health benefits of velvetleaf include treating digestive disorders, chronic inflammation, and skin-related issues, and it also acts like a pain reliever. Velvetleaf is very beneficial to women since it helps women suffering from PMS symptoms. Velvetleaf is not popular in the United States, making it hard to find unless in select stores that offer alternative means of medication.
Verdolaga
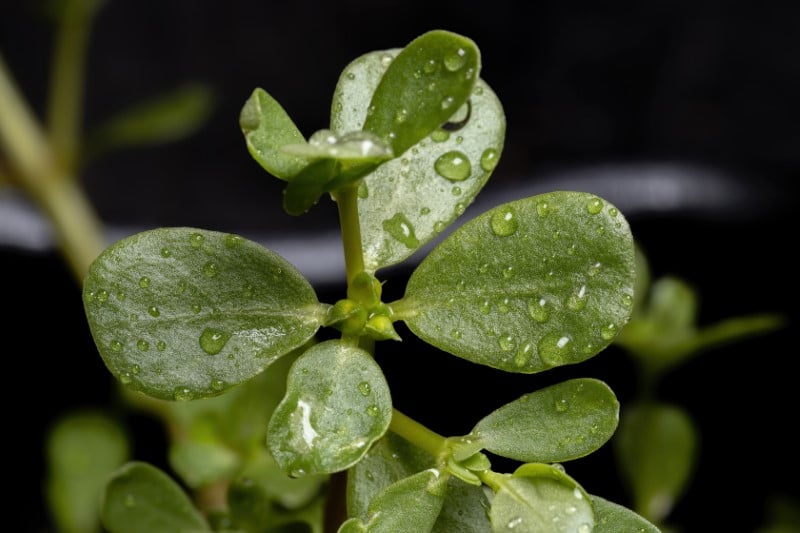

Verdolaga is an annual succulent vegetable plant that is a member of the Portulacaceae family. The common names of the verdolaga include common purslane, parsley, Mexican parsley or little hogweed, and the scientific name is Portulaca oleracea. The verdolaga flowers are usually yellow, while the stems and the leaves are smooth and reddish. The leaves are mostly clustered at the stem ends and joints. The verdolaga plant produces pods that enclose the seeds. The pods only open up when the seeds are mature.
Verdolaga is an edible vegetable with a salty and slightly sour aftertaste. Verdolaga is a very common delicacy throughout Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, Mexico and Asia. The stem flower buds and leaves of the verdolaga plant are all edible, both raw or cooked. Fresh verdolaga can be served as a salad, and when cooked, it can be cooked like spinach or stir-fried. Verdolaga is also very tasty when used to prepare soups or stews. The seeds of the verdolaga plant can be used to make seedcakes. In Greece, verdolaga, the leaves and stems are mixed with olive oil, garlic, cheese, tomato and onion and added to salads. In Turkey, verdolaga is missed with yogurt to create a tzatziki variant. In Portugal, verdolaga is used to prepare a traditional soup known as sopa de beldroegas, which can be escorted with poached eggs, goat cheese, and soaked bread.
Verdolaga contains antioxidants, minerals and vitamins that immensely benefit the body. Examples of the nutritional contents and health benefits include vitamin C, which helps stimulate the production of collagen as well as helping speed up the healing of various injuries sustained. Verdolaga contains beta-carotene, an antioxidant that helps reduce the number of free radicals in the body, thus preventing the body cells from being damaged. Calcium and magnesium help prevent osteoporosis and improve bone health while preventing complications caused by aging. Also, verdolaga contains vitamin A which is essential to eye health and boosting the immune system.
The Final Letter
Vegetables are a must-have in your diet, so the list above will guide you through the various types of vegetables available and the healthy goodness we obtain from the vegetables. You can also use the list above and challenge yourself to come up with new recipes involving the above-listed vegetables. Remember that before trying an exotic vegetable, ensure you consult your nutritionist or doctor about the side effects of the vegetable on your health.