All The Vegetables That Start With F
Important Note: When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Content, pricing, offers and availability are subject to change at any time - more info.
Vegetables is a blanket term for all edible plant parts, mostly leaves, roots, and seeds. Some vegetables are found growing in the wild while others are cultivated. However, nutritionists recommend that you consume vegetables daily due to their rich nutritional value.
Having the same vegetables frequently appearing on your menu can be very boring. It is always a nice experience to try out new delicacies and recipes to enrich yourself with various nutritional benefits. For those interested in venturing into new recipes, here is a list of all vegetables that start with F.
- Frisee
- Fennel
- French Bean
- Fenugreek
- Fiddlehead
- Fava Bean
- Flat Cabbage
- Field Blewit
- Fat Hen
- French Sorrel
- False Daisy
- Frilled-Leaf-Mustard
- The Final Letter
Frisee
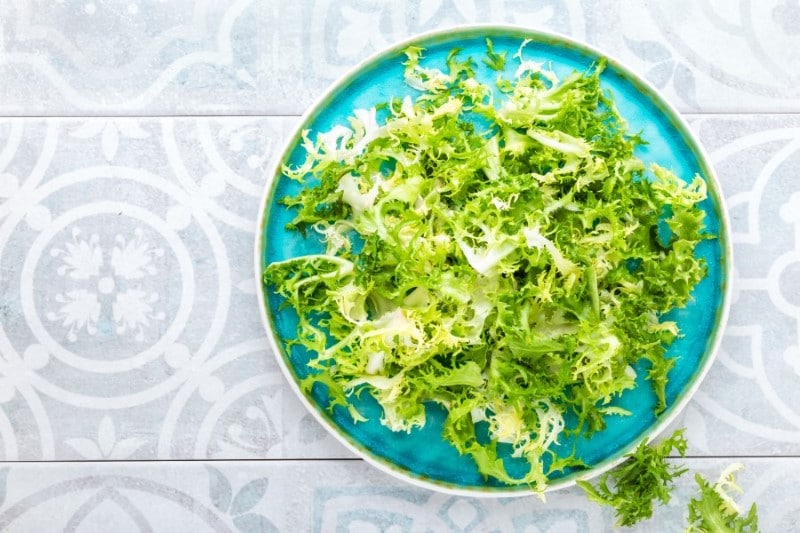

The scientific name of frisee is Cichorium endivia var. crispum. Frisee plant is available in the Netherlands, United Kingdom, and France. Frisee vegetables belong to different families, with frisee belonging to the chicory family. These vegetables also have the name curly endive. They resemble lettuce but are different from lettuce in taste and appearance.
Frisee has narrow, curly green, fizzy leaves with a pale yellow hue near its core. These frisee vegetables have green outer leaves and a yellow heart/hue with a very bitter taste. Generally, the curly endive vegetables have a bitter and pepper-like flavor.
You can prepare frisee as salads by cutting the leaves into bite-size pieces using either hand or knife to make it easy to pick them up with a fork. Frisee can also be cooked. However, when cooking this vegetable, slice the leaves into very small pieces using a knife and remember to avoid the heart of the frisee, which is packed with bitterness. You can also cut the frisee leaves and add them to meat stew.
Frisee vegetables are a good source of Vitamin A, which helps maintain good vision and prevent cell damage by neutralizing free radicals in the body. These vegetables also contain Vitamin C, which is essential in strengthening the immune. Vitamin K traces in the frisee vegetables help provide the blood with the ability to form clots when skin is cut.
Fennel
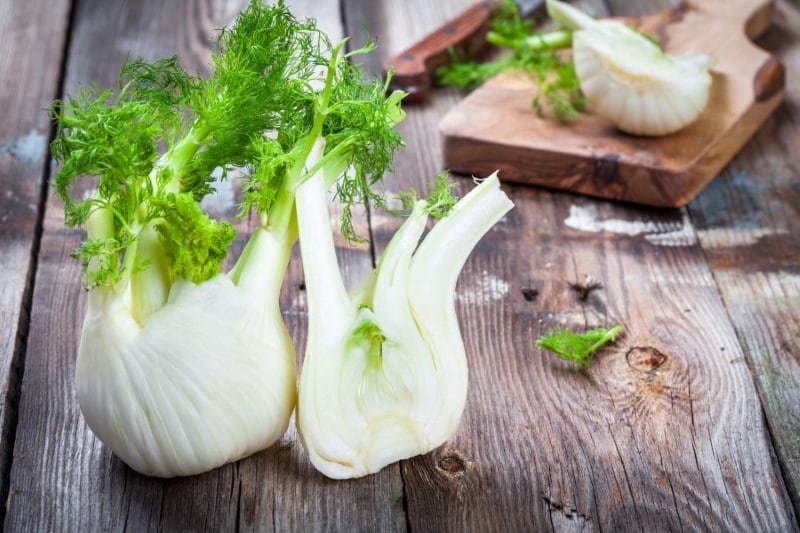

The scientific name of the vegetable fennel is Foeniculum vulgare. These vegetables are sourced from a flowering herb that belongs to the carrot family. These herbs are found ingeniously growing on the Mediterranean shores and in some regions of California, Australia, and Italy.
The part of the plant considered a vegetable is the stalk bulb. This bulb is located at the base of the plant and above the ground. The bulb is thick, white, and crispy with a fresh, anise, and aromatic flavor.
The bulb of the fennel is widely used in many recipes. To prepare a funnel, wash the vegetable bulb, cut the root end, chop into quarters, and remove the core from each quarter with a knife; peel apart the layers and cut into your desired size and shape.
Funnel is a sweet vegetable with a slight taste of licorice and can be used in many dishes. This vegetable can be prepared and eaten raw in salads. You can also cook funnel in soups, stews, or pasta dishes.
The bulb of fennel is rich in health benefits. Eating fennel vegetables will give you strong and healthy bones due to the calcium and sodium minerals. The calcium, magnesium, and potassium minerals found in the funnel vegetables are essential in maintaining your blood pressure. Funnel vegetables are also rich in fiber, which helps you improve your heart health by lowering your cholesterol levels.
French Bean
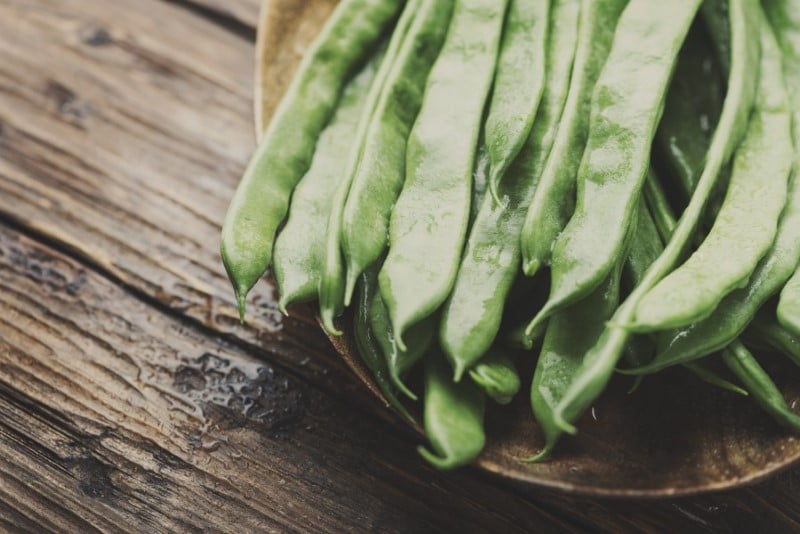

The scientific name of the French bean is Phaseolus vulgaris. The other common names of the French beans are string beans or green beans. These green beans belong to the legume family but are considered vegetables. French beans thrive in warm and sunny positions. Originally they originated from South and Central America, but China is the largest producer.
French beans are small, slender green pods that are either straight or curved with pointed ends. The pods are tender, smooth, firm, and fleshy, with tightly enclosed soft green or white seeds at the center. The French beans are a common vegetable well-known for their sweet, subtly earthy, and vegetal taste with a faint grassy aroma.
French beans require little time to cook. To enjoy their wonderful taste, avoid overcooking the french beans. You can use little water to steam the beans or quickly fry them in olive oil to maintain their shape, color, and crispy flavor. You can fry the French beans or stew them and serve them alongside starch meals or meat.
To prepare these French beans, trim both the pointed ends, eliminate the strings on the side for mature beans, then chop into pieces or cook them as a whole. Remember to always go for the younger but mature pods of the French beans, which are tastier, tender, and without strings.
French beans are packed with dietary fibers, which make you feel full for a long time, reducing the urge to eat, thus helping weight loss frequently. The Vitamin C and A present in the french beans are beneficial to maintaining a healthy soft, and moisturized skin. The french beans also contain calcium, potassium, and Vitamin K, which are essential in building and maintaining strong bones that don’t fracture easily.
Fenugreek
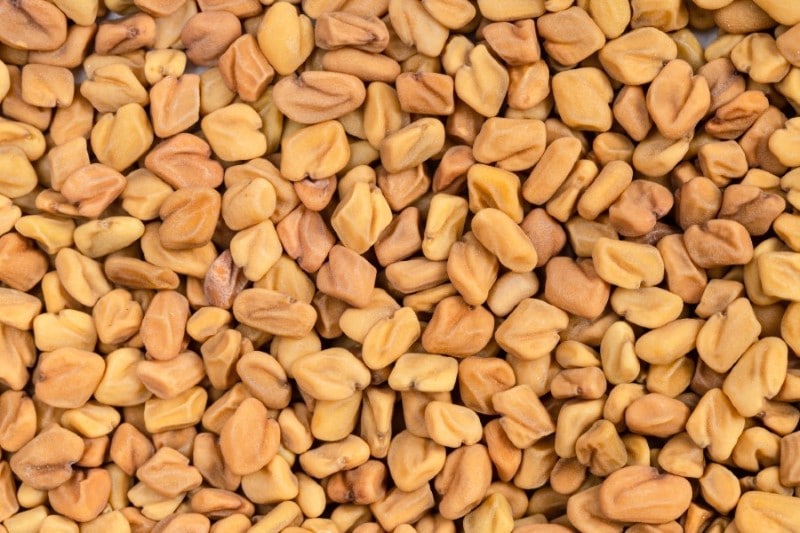

The scientific name of fenugreek is Trigonella Foenum- graecum. The fenugreek plant belongs to the family of peas. They are found in South Asia, the Mediterranean, France, North Africa, and mostly warm weather regions.
The fenugreek leaves are small and have obovate to oblong leaflets. Both the seeds and the leaves are edible, but the leaves are what we consider vegetables. In North Africa, Middle Eastern countries, and India, fenugreek is used as herb and spice. This vegetable can be used fresh or dried.
Fenugreek leaves can be used in sauces, curries, soups, and vegetable dishes. The seed can also be roasted and crushed, and the powder is used as a spice in meats and soups. Fenugreek leaves are less bitter and are used to add flavor to meals and soups. You can also blend the leaves into butter as baste.
Fenugreek can lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Research has also shown that fenugreek can act as a natural painkiller by reducing the pain in women with painful menstrual periods. Fenugreek has other health benefits like boosting sexual and reproductive health and weight loss.
Fiddlehead
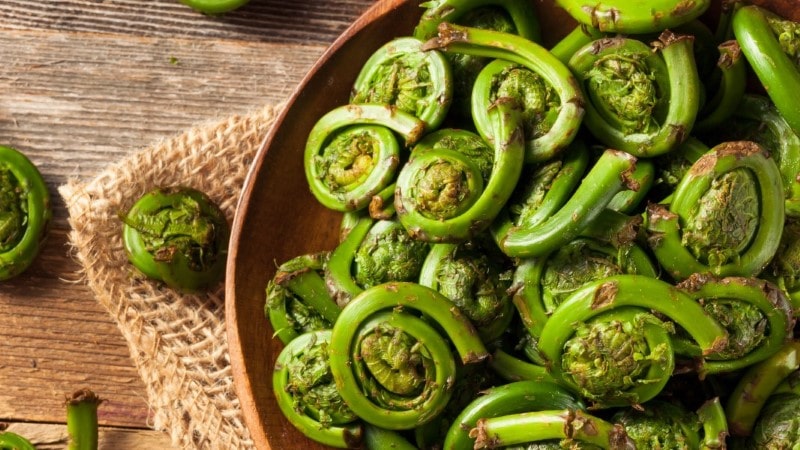

The scientific name for the fiddlehead is Matteuccia struthiopteris. The vegetable fiddlehead is the tightly coiled ends of fern leaves. These fern plants grow in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Asia.
The fiddlehead are green vegetables that have small, tightly wound-up coils. These vegetables are sweet-bitter and have a snappy grassy taste. However, the only safe fiddleheads for consumption are those harvested from the Ostrich fern fiddleheads. Other varieties of fern plants have fiddleheads that are toxic.
Fiddleheads that are green and have tight coils are best for use. Wash the fiddleheads in cold water and immediately cook them. Remember not to eat raw fiddlehead vegetables because they contain some traces of toxins which get destroyed when the fiddleheads are well cooked in the heat.
Fiddlehead vegetables are steamed or quickly fried in low fat and added to buttery dishes. You can also roast the fiddlehead ferns or cook them in soup.
Fiddlehead vegetables are rich in Vitamin A, which helps prevent night blindness and the degeneration of cells due to age. These vegetables also have traces of iron and copper, which are essential in forming new body cells. The fiddlehead vegetables contain Vitamin C, which gives the body ability to fight infections and help destroy free radicals in the body, which cause cancer.
Fava Bean
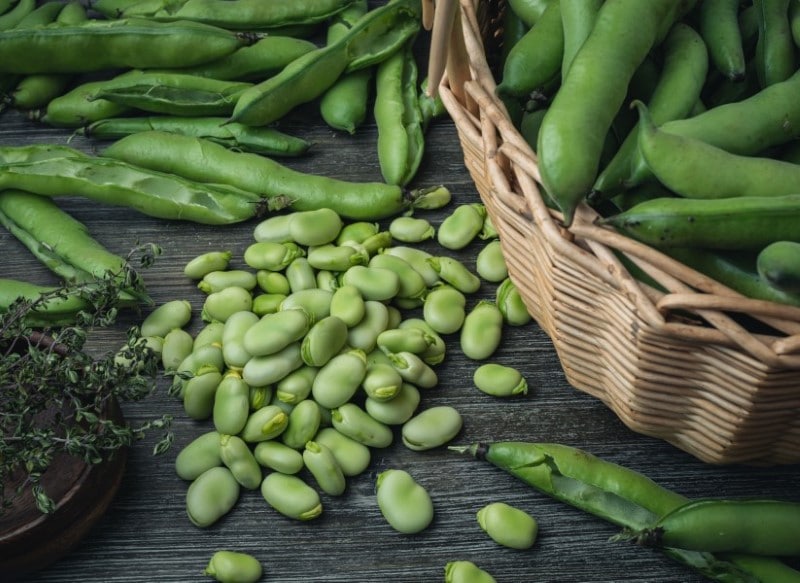

The scientific name of fava bean is Vicia faba. The fava bean is a legume that belongs to the bean (fabaceae) family, mainly grown for its seeds and pods. The fava bean plant is native to South Asia and the Mediterranean and is cultivated in North Africa, North America, and South America. Canada is the largest producer. Favor bean plant thrives mostly in cold weather.
Fava bean is also referred to as broad bean or horsebean. These legumes are cultivated for human and animal consumption and used as a vegetable, whether fresh or dried. Fava beans can be black-brown or greenish-black in color. These beans have a mild taste and are less starchy. These legumes have a nutty, creamy, earthly, and sweet-bitter taste.
Preparation of fava beans is essential before using them. First, open the pod, remove the beans, wash and blanch the beans by boiling in water until tender, and chill the beans to stop the cooking process. You can then remove the skin if the beans are large and mature.
You can eat the fava beans fresh or dried. Deep the beans in coarse salt, olive oil, and pepper, and serve to enjoy the fava beans raw. Small immature beans are steamed or boiled and served with a cheese source. The fava beans can also be fried in little olive oil and sprinkled with a little lemon juice and cream.
Fava beans contain folates, which help improve cardiovascular health, boost immune functions, and form red blood cells. These beans are also rich in fiber, which is essential in lowering cholesterol levels and maintaining a healthy blood sugar level in your body. Fava beans also contain Vitamin B1, which is beneficial in maintaining a healthy nervous system and controlling the metabolism process.
Flat Cabbage
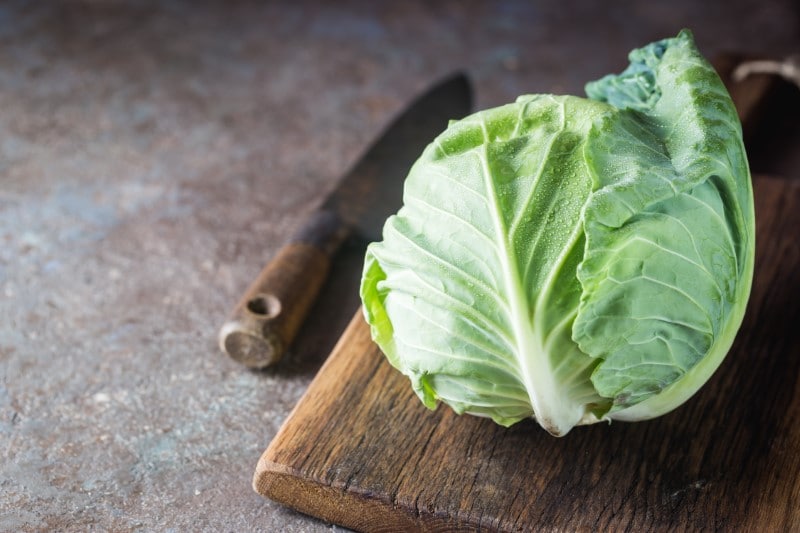

The scientific name of flat cabbage is Brassica oleracea var. capitat. The flat cabbage is believed to originate in Taiwan. These cabbages are found in Northern Europe, Asia, Canada, and the United States. The flat cabbage thrives in cooler climates.
The flat cabbage is large and takes an oblate shape. The cabbage has flat heads that consist of thin layers of loosely packed leaves. These leaves are broad, smooth, white, or pale green and have a smooth texture. The flat cabbage is tender, juicy, crunchy, and sweet with a mild taste. However, the head of the flat cabbage is more compact and heavier than how it looks.
The flat cabbage’s outer leaves must be removed before using the vegetable. You can choose to steam or boil the cabbage. However, it is advised to cook the cabbage in low heat to preserve its crunchy sweet taste. The flat cabbage can also be chopped, mixed with lettuce, and eaten raw in salads or served with fish fillets. The flat cabbage can be cut into very fine pieces and added on top of soups for flavor.
Cabbage is found to contain a compound called sulforaphane, which gives these vegetables their cancer-fighting ability. Cabbages are also beneficial to the health of the heart. These vegetables are rich in polyphenol, which helps reduce blood pressure and lower your risk of cardiovascular diseases. Flat cabbage is high in water and fiber content, giving these vegetables the ability to prevent constipation and maintain a healthy digestive tract.
Field Blewit
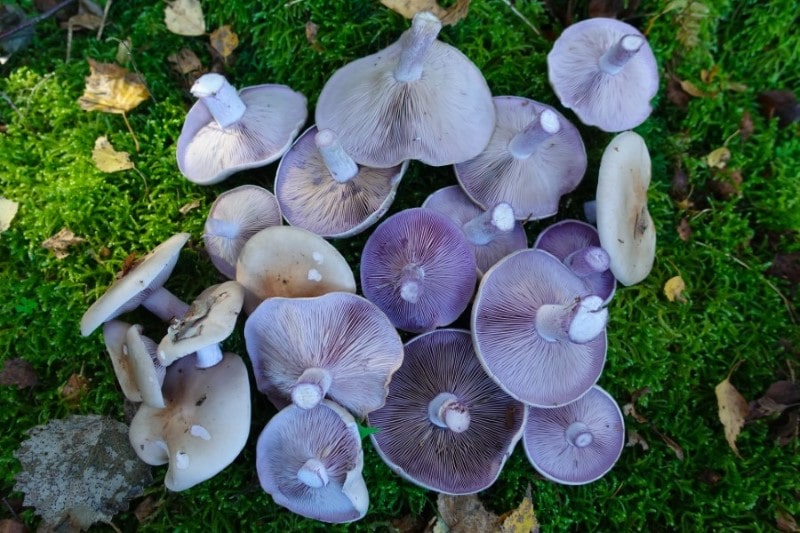

The scientific name for field blewit is Lepista personata. These mushrooms thrive in cold weather and are commonly found in North America. These mushrooms often grow beneath oak tree leaves, on wood debris, or under various trees in open areas.
Field mushrooms have varying tastes depending on the place they grow on. However, these mushrooms can possess a unique fragrance with a sweet aroma. The taste of the flesh of field mushroom is incomparable to other vegetables because it is unique and distinctive. Blewit mushrooms take a convex shape and have a lavender color that fades with age.
Field mushrooms are never eaten raw and must be thoroughly cooked before consuming them. Preferably use the young mushrooms and cook. You can fry them with onions and oil and serve them alongside meat. The field blewit can also be cooked to make stew served with starchy meals.
Field mushrooms contain beta-glucan fibers, which help strengthen the immunity, help fight disease and stop tumor formations in the body. Field blewit mushrooms are high in potassium, which helps reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by maintaining well-balanced blood pressure. These mushrooms also have traces of selenium mineral, which helps maintain the liver’s enzyme function, reduce inflammation and lower the chances of growing cancer cells.
Fat Hen
The Scientific name of fat hen is Chenopodium album. The fat hen is an annual herb commonly referred to as wild spinach or goosefoot. Fat hen is cultivated in Africa and Asia as a vegetable while being considered a weed in Europe and America. This plant is commonly found growing on disturbed lands, waste places, or roadsides.
Fat hen is an edible herb with leaves resembling a goose’s foot, as the name suggests. The leaves have tiny hairs with a powdery, waxy surface making them hard to get soaked by water. The fat hen vegetables have leaves that are grey-green with rugged edges.
These wild herbs are edible and taste like spinach. Fat hen vegetables are often used as a substitute for spinach. The leaves have no strong odor and taste like cabbage. The young leaves of fat hen are used fresh in salads while the old leaves are cooked or steamed in little water.
The fat hen plant is often mistaken for a similar plant in looks called the black nightshade, which is poisonous. The edible leaves of the fat hen plant contain high amounts of Oxalic acid, making them dangerous if eaten in excess.
Fat hen vegetables are rich in Vitamin A, which is essential in maintaining healthy vision and helps the normal functioning of your organs and immune. Fat hen vegetables also contain calcium mineral, which is good for regulating normal heart rhythms and nerve functions and maintaining strong, healthy bones. Phosphorus present in the fat hen vegetables help manage how your body stores and uses energy.
French Sorrel
The scientific name for French sorrel is Rumex scutatus. The French sorrel vegetables are harvested from a wildly growing mound-shaped plant. This plant grows in temperate regions and belongs to the buckwheat family.
The leaves of the plant are what are considered vegetables. French sorrel leaves are lance-shaped and shiny green. These vegetables are very acidic, sour, spicy, and have a flavor like a lemon.
French sorrel’s small immature leaves are used raw because of their tenderness. You, however, should avoid a french sorrel-only salad because of its bitter taste. The larger mature leaves can be used in cooking and flavor addition to meals like eggs, whole grains, and potatoes. French sorrel leaves can be used as a garnish for fish and veal or as a meat tenderizer. French sorrel vegetable is best served in combination with other meals.
French sorrels are rich in Vitamin C, which is essential in building a strong immune and helps your body fight infections. The french sorrels also contain Vitamin A, which improves reproductive health and maintains healthy skin and good vision. These sorrel vegetables are rich in fiber, essential in lowering the chances of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
False Daisy
The scientific name for false daisy is Eclipta prostrate. They are majorly found in the tropics. False daisy grow and thrive in almost all parts of the world, including America, except Antarctica. This annular crop has to ascend prostrate stems which are purplish.
False daisy can be blended to make juice which has wide nutritional benefits. These vegetables can also be mixed with coconut oil to make a paste used to deal with skin diseases for medicinal purposes.
The false daisy vegetable is beneficial and has been used as a traditional medicine to cure some illnesses and conditions. The false daisy is good for improving digestion, preventing constipation, and ensuring a healthy digestive tract. These vegetables are also essential in maintaining the stable health of the heart by lowering your chances of cardiovascular diseases. These vegetables can inhibit the growth of cancer cells, lowering the risk of cancer. False dais can boost the health of the eyes and vision.
Frilled-Leaf-Mustard
The scientific name of frilled-leaf-mustard is Brassica juncea. This perennial herb is considered to have originated from Western and Central China and India. It is found growing in Central Africa, India, Canada, and the United States. The mustard leaf is grown in subtropical and temperate climates.
The leaves of this plant are green or with a whitish bloom. These leaves are considered vegetables and are oblate-shaped with frilled edges that are rough.
First, to cook frilled leaf mustard vegetables, wash the leaves and rip out the stems to remain with leaves only. You can use young, tender leaves, cut them into pieces, sprinkle a little vinegar, and add them to other greens and vegetables to make salads.
The mustard vegetables can be cooked with little water and combined with mashed potatoes or legumes that have been pureed. You can choose to steam the mustard leaves and cut them into small pieces, fry them quickly in little oil, combine with butter and serve.
Filled leaf mustard is rich in vitamin A, which helps moisturize the skin and boost the eyes’ health. The mustard leaves also contain Vitamin C, which is essential in boosting the body’s immunity, keeping you from frequent diseases and infections. These vegetables are also packed with potassium mineral that helps maintain healthy functions of nerves and regulate fluid balance.
The Final Letter
Vegetables are rich in essential nutrients that can help you build a strong, healthy body. You are now well informed of the hidden gem beneath all vegetables that start with F. Why don’t you challenge yourself to take a step and try out each one of the listed vegetables. Remember, it is always safe to buy the wild growing herbs from the store and market to avoid confusing them with lookalikes, which could be toxic.